Becoming a Tax Filer in Pakistan: Guide for Everyone
Unlock Financial Benefits: Step-by-Step Guide to Becoming a Tax Filer in Pakistan

In Pakistan, becoming a tax filer is an essential step toward becoming financially responsible and making a contribution to the growth of the nation’s economy. In order to become a tax filer, you must first register with the FBR and then file an income tax return. This is a civic duty that also carries with it some legal requirements. This thorough guide will shed light on the way forward for individuals and companies that are looking to manage the complexities of Pakistan’s tax system. Understanding the necessary steps to become a tax filer is crucial, regardless of whether you are a paid professional, the owner of a firm, or a freelancer.
What Does Tax Filer Mean in Pakistan?
In Pakistan, a tax filer refers to an individual or company that has completed the registration process with the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) and has effectively filed their income tax return for a designated fiscal year. Tax filing is a legal requirement for both individuals and companies in Pakistan who have earned taxable income.
Steps To Become a Tax Filer in Pakistan
Join us as we break down the process of becoming a tax filer into clear, practical stages. This will help you to complete your tax duties. Moreover, you’ll be able to play a proactive role in the economic progress of Pakistan.
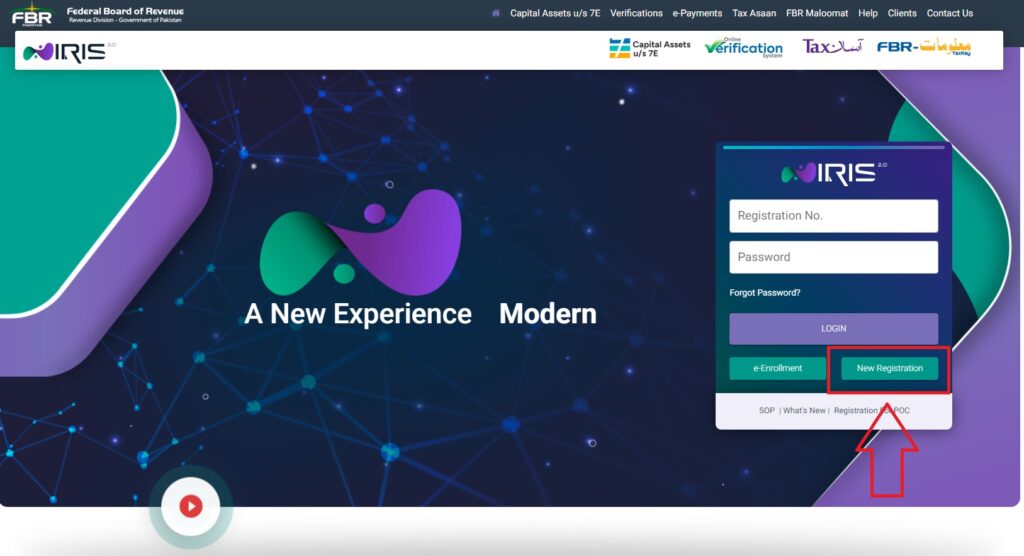
First and foremost, as a Pakistani citizen, having a CNIC is a prerequisite for tax registration.- To register online, go to the FBR’s IRIS web page and click on New Registration.
Source: FBR IRIS - Depending on your source of income, select the right taxpayer category. This could apply to a single person, a group of people (AOP), or an organization.
- Provide accurate information on the online registration form, including your personal information and sources of income.
- Submit the documents for verification. The FBR may ask for documents like pay slips, CNICs, and information about business registration.
- After the verification of your documents, you will receive a tax certificate with your National Tax Number (NTN).
- For tax purposes, NTN is your unique identifier.
After your NTN has been generated and the tax certificate has been issued, you can use these as evidence that you have become a tax filer. Next, you’ll need to file your income tax returns via the Iris Portal at the end of every fiscal year against the same NTN number.
The NTN number is usually the CNIC number for an Salaried Persons.
Have you ever been a victim of cybercrime in Pakistan? Learn How To Lodge Cybercrime Report in Pakistan.
Types of Taxpayers in Pakistan
In Pakistan, taxpayers are categorized according to the nature of income that people are earning. These categories are:
- Salaried Individuals
- Association of Persons (AOP)
- Self-Employed Individuals
- Companies
1: Salaried Individuals
Salaried individuals are the people who earn a regular income as part of their pay for their employment. Persons employed in either the public or private sector fall under this category.
Tax Considerations
- Salaried individuals are subject to income tax on their salary income.
- Employers deduct tax at source (TDS) from the salaries of employees based on the applicable tax rates.
- Salaried individuals are required to file an annual income tax return to report any additional income, deductions, or exemptions.
2: Association of Persons (AOP)
The Association of Persons (AOP), or Business Individuals, refers to individuals who are involved in business activities. This category includes two types of individuals: sole proprietors and members of an Association of Persons (AOP). Sole proprietors are individuals who run their businesses independently. Whereas, AOPs are individuals who come together to engage in business activities collectively.
Tax Considerations
- Business individuals are liable to pay tax on their business profits.
- They are required to maintain detailed records of income, expenses, and profits related to their business activities.
- Filing an annual income tax return is mandatory, and the return should include information about the business’s financial performance.
3: Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed Individuals refer to individuals who work for themselves and are not employees of a business or organization. They are responsible for providing their own services and generating their own income. Examples of self-employed professionals include doctors, lawyers, consultants, and freelancers.
Tax Considerations
- Self-employed professionals are liable to pay tax on their professional income.
- They must maintain records of their professional earnings, expenses, and any deductions applicable to their profession.
- Filing an annual income tax return is mandatory, and it should accurately reflect their professional income and financial details.
4: Companies
Companies refer to legal entities that have been registered under the Companies Act. Types of entities like private limited companies, public limited companies, and various other corporate entities fall under this category.
Tax Considerations
- Companies are subject to corporate income tax on their profits.
- Corporate tax rates are applied to the net profits of the company.
- Companies must file an annual income tax return, disclosing financial statements, profit and loss statements, and tax computations.
It is important to have a clear understanding of the specific tax obligations that apply to each category. This will help you to ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations. To ensure that your tax filing is accurate and in compliance with tax regulations, you must seek professional advice. This applies to both individuals and entities. By consulting with a tax professional, you can receive expert guidance on how to optimize the available tax benefits that you may be eligible for. Seeking professional advice will help you navigate the complexities of the tax system and ensure that you are making the most informed decisions regarding your taxes.
Check Out: Common Misconceptions about Tax Filing in Pakistan
Final Wrap
In Pakistan, becoming a tax filer is a necessary first step toward economic independence and civic engagement. By following the steps explained here, readers will be able to confidently deal with the IRIS’s complex tax requirements. Filing taxes is not only the right thing to do, but it also has many practical advantages, such as allowing you to participate in the economy and have access to financial services. As we wrap up this blog, it’s important to remember that paying your fair share of taxes is an obligation for everyone in this country. By following the steps outlined above and staying informed about any updates from FBR, individuals can embark on their tax filing journey, contributing to a more transparent and prosperous financial landscape in Pakistan.
PTA Taxes Portal
Find PTA Taxes on All Phones on a Single Page using the PhoneWorld PTA Taxes Portal
Explore NowFollow us on Google News!